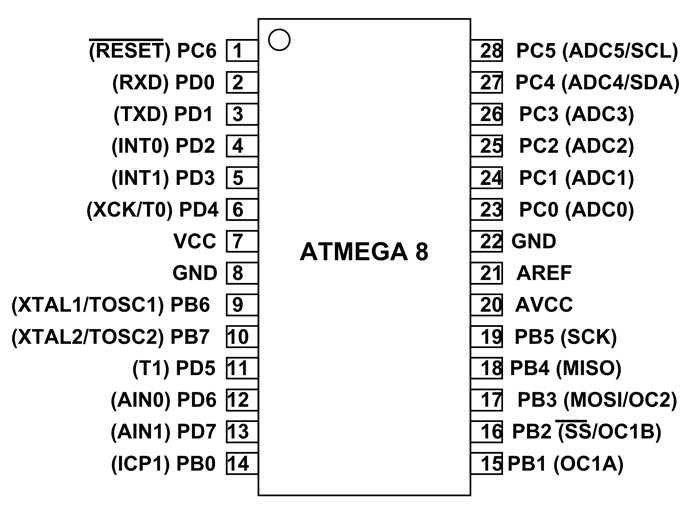
Atmega8 Uart Program
- Atmega8 Uart Program Download
- Atmega8 Uart Code Example
- Atmega8 Uart Program Free
- Atmega8 Uart Programming
| Serial Communication tutorial |
This tutorial focuses to teach you how to program AVR Serial Communication (UART). UART plays an important role in almost every embedded applications which we see in our day to life and hence it was considered to be very important concept in every Microcontroller.
- USB ASP Programmer & Atmega Programming – Tutorial #3. It’s assumed that you have procured one USBasp Programmer from your trusted component vendor! Connecting the programmer to your computer comprises of two steps. First step is the physical connection of the programmer to the USB port using a suitable USB cable, and the second step is the.
- Atmega8 Uart Program. 0 Comments var q atmega8uartprogramSDSDHC Card Interfacing with ATmega. 2 implementation. Here is my project on interfacing of.
USB ASP Programmer & Atmega Programming – Tutorial #3. It’s assumed that you have procured one USBasp Programmer from your trusted component vendor! Connecting the programmer to your computer comprises of two steps. First step is the physical connection of the programmer to the USB port using a suitable USB cable, and the second step is the.
The above design demonstrates the usage of UART to send and receive data via hyperterminal as well display the received data in 1 16×2 LCD. As we all know Microcontroller works in TTL logic which is not compatible with the PC so we have to employ a level converter IC MAX232, read more about the working of IC MAX232.
REGISTERS USED IN AVR SERIAL COMMUNICATION:
In AVR there are five registers which are meant to use for Serial Communication such as UDR, UBBR , UCSRA, UCSRB, UCSRC. Lets see the functions of these registers briefly.
UDR:
| UDR Register |
UDR or USART Data Register is meant for writing and receiving the data through the UART. In this there are two shift registers referred to as Transmit Shift register and Receive Shift register with each having a separate buffer register. When the data is written to UDR it will be transferred to Transmit Data buffer register and when we read the contents of the Receive Data buffer register is returned.
UBRR:


In AVR the baud rate of the UART is programmable and it is achieved by means of this UBRR register. It is 16 bit register classified into lower UBRRL and higher UBRRH out of which 12 bit is usable The formula governing the relation between the value of UBRR and Oscillator is
Baud Rate = (Oscillator Frequency / (16( UBRR Value +1))
So for a 8MHz oscillator frequency and 9600 baud rate the value need to be loaded in the UBRR will be
UBRR = (8MHZ /16(9600))-1
=(500KHz/ 9600) – 1
= 51 ( equivalent hex 33)
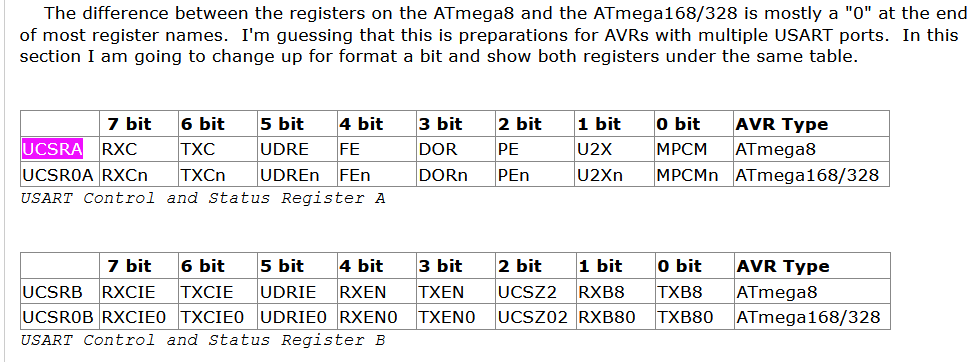
UCSRA:
| UCSRA Register |
UCSRB:
| UCSRB Register |
UCSRC Register:
| UCSRC Register |
STEPS TO PROGRAM UART:
- Load the hex value in the UBRR Register for the Baud rate you are about to use.
- Set the bits in the registers UCSRA, UCSRB & UCSRC based on your usage requirement.
- For Transmission Place the data in the UDR register and check for the appropriate flag to set in the UCSRA regsiter
- Clear the Flag for further transmission.
- For receiving the data, wait for the Receive flag to set in the UCSRA register and then read the UDR register to obtain the received data for processing or display.
- Clear the Flag for further data reception.
CODE:
JLCPCB - Only $2 for PCB Prototype (Any Color)
24 Hours fast turnaround, Excellent quality & Unbeatable prices
Up to $20 shipping discount on first order now: https://jlcpcb.com/quote
Related content
Related content
Atmega8 Uart Program Download
If You come there from internet search i assume You already know what is PWM and where it can be used, so in this post I’ll only explain how to use 8 bit timer in Atmega8 to generate PWM signal and control frequency, polarity and duty cycle.
PWM can be generated from 16-bit Timer/Counter1 or 8-bit Timer/Counter2 but this time I’ll only explain 8-bit Timer/Counter2Fast PWM Mode.
In this picture from Atmega8 documentation Fast PWM mode is explained. Counter(8bit) counts from 0x00 to 0xFF and restarts from 0x00. In not inverting mode OC2 is cleared when counter match value in OCR2 register and set at 0x00. In inverting mode OC2 is set when counter match value in OCR2 register and cleared at 0x00.
From this all turns out that PWM duty cycle depends on OCR2 register. In not inverting mode duty cycle = OCR2/256*100% and it’s 50% if OCR2 is 0x80(middle between 0x00 – 0xFF).
In every PWM period counter must count 256 steps, so frequency of signal is 256 times lower than counter clock from prescaler. PWM frequency = Atmega clock frequency/timer prescaler(1,8,32,64,128,256)/256. With 4 MHz crystal maximum(without prescaler) PWM frequency is 15 625Hz.
Register setup
For example 15 625 Hz, 50 % duty cycle, non-inverting mode PWM signal generation.
1. OCR2=0x80(128); As mentioned before duty cycle = OCR2/256*100%
2. TCCR2=0x69;
3. DDRB=0x08; PWM signal is outputted by toggling level of PORTB pin 3.
DDRB sets it as output.
Atmega8 Uart Code Example
All together:
#include <iom8.h>
int main( void )
{
DDRB=0x08;
OCR2=0x80;
TCCR2=0x69;
while (1) {};
}
Result:
Atmega8 Uart Program Free
~10% duty cycle, 61 Hz.
#include <iom8.h>
int main( void )
{
DDRB=0x08;
OCR2=0x1A; // 256/10=25,6 26 in hex = 1A;
TCCR2=0x6E; // 256 prescaler
while (1) {};
}
Result:
And there is demo program and *.hex file for PWM demo seen in video.
Atmega8 Uart Programming
Atmega8 PWM demo program (1.8 KiB, 8,281 hits)